코딩테스트/알고리즘 정리
인접 행렬과 인접 리스트
까루카라
2024. 3. 20. 18:32
그래프를 구현하여 표현하는 방법에는 여러가지가 있지만 일반적으로 인접행렬과 인접리스트 방식이 있다.
이 두가지 방식은 서로 정반대의 특징을 갖기 때문에 한 방식의 장점이 다른 방식의 단점이 되는 경우가 나타난다.
따라서, 구현하려는 알고리즘, 그래프의 종류에 따라 적절하게 사용하여야 한다.
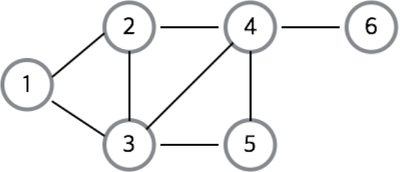
인접 리스트를 이용한 그래프 구현
package boj.study.week6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class adjacencyList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int initSize = 6;
ListGraph adjList = new ListGraph(initSize);
adjList.put(1, 2);
adjList.put(1, 3);
adjList.put(2, 3);
adjList.put(2, 4);
adjList.put(3, 4);
adjList.put(3, 5);
adjList.put(4, 5);
adjList.put(4, 6);
adjList.printGraphToAdjList();
}
}
// 그래프(리스트) 클래스
class ListGraph {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> listGraph;
// 생성자
public ListGraph(int initSize) {
this.listGraph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
/**
* 그래프 초기화
* put(int x, int y) 에서 입력되는 정점의 값은 0 이상의 정수이나
* ArrayList의 index는 0 부터 시작이므로
* ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException을 방지하기 위해
* 정점을 담는 인접리스트의 size는 1을 더하여 초기화해줌
* ex) initSize = 3
* graph[0] -> 2 -> 3
* graph[1] -> 1 -> 3 -> 4
* graph[2] -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5
* graph[3] -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5
*/
for (int i = 0; i < initSize + 1; i++) {
listGraph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> getGraph() {
return this.listGraph;
}
// 그래프 추가 (양방향)
public void put(int x, int y) {
listGraph.get(x).add(y);
listGraph.get(y).add(x);
}
// 그래프 추가 (단방향)
public void putSingle(int x, int y) {
listGraph.get(x).add(y);
}
// 그래프 출력 (인접 리스트)
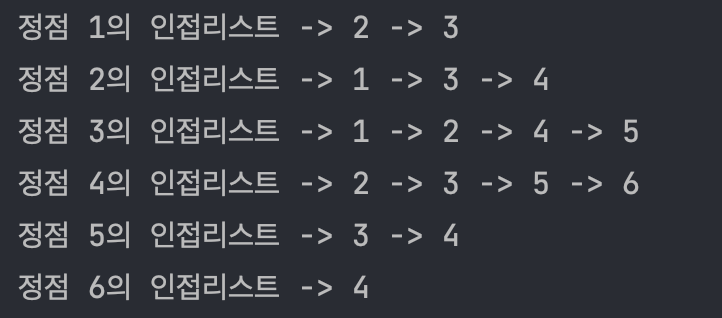
public void printGraphToAdjList() {
for (int i = 1; i < listGraph.size(); i++) {
System.out.print("정점 " + i + "의 인접리스트");
for (int j = 0; j < listGraph.get(i).size(); j++) {
System.out.print(" -> " + listGraph.get(i).get(j));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
인접 행렬을 이용한 그래프 구현
인접 행렬은 N x N 행렬로 graph[i][j]가 true라면 i에서 j로의 간선이 있다는 것을 의미
정점의 개수가 V라면 V^2 크기의 2차원 배열을 생성하여 1과 0을 사용하여 true / false를 구분하여 값을 저장한다.
양방향 인접행렬의 경우 대칭 행렬의 형태로 구성된다.
package boj.study.week6;
public class adjacencyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int initSize = 6;
ArrGraph adjArr = new ArrGraph(initSize);
adjArr.put(1, 2);
adjArr.put(1, 3);
adjArr.put(2, 3);
adjArr.put(2, 4);
adjArr.put(3, 4);
adjArr.put(3, 5);
adjArr.put(4, 5);
adjArr.put(4, 6);
adjArr.printGraphToAdjArr();
}
}
class ArrGraph {
private int[][] arrGraph;
public ArrGraph(int initSize) {
/**
* 그래프 초기화
* put(int x, int y)에서 입력되는 정점의 값은 0 이상의 정수이나
* 배열의 indexsms 0 부터 시작이므로
* ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException을 방지하기 위해
* 정점을 담는 인접행렬의 행과 열 size는 1을 더하여 초기화 해줌
*/
this.arrGraph = new int[initSize + 1][initSize + 1];
}
// 그래프 return
public int[][] getGraph() {
return this.arrGraph;
}
// 그래프 추가(양방향)
public void put(int x, int y) {
this.arrGraph[x][y] = this.arrGraph[y][x] = 1;
}
// 그래프 추가(단방향)
public void putSingle(int x, int y) {
this.arrGraph[x][y] = 1;
}
// 그래프 출력 (인접행렬)
public void printGraphToAdjArr() {
for (int i = 1; i < arrGraph.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < arrGraph[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(" " + arrGraph[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
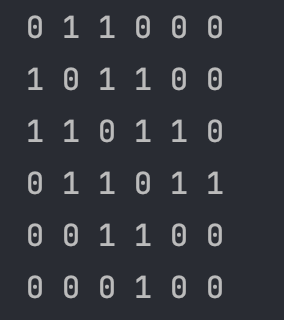
인접 행렬과 인접 리스트의 차이
| 정점 간의 간선 여부 | 공간 복잡도 | |
| 인접 행렬 | 정점 v1, v2에 대해 한 번의 접근으로 확인 가능 | V개의 노드 표현을 위해 V^2 만큼의 공간이 필요 인접 노드를 찾기 위해선 모든 노드를 순회해야 함 공간복잡도 : O(V^2) |
| 인접 리스트 | 리스트의 처음부터 하나씩 확인해야 함 | V 개의 리스트에 간선 (E) 만큼 원소가 들어있음 인접 노드를 쉽게 찾을 수 있음 공간복잡도 : O(V + E) |
인접 행렬과 인접 리스트가 사용되는 경우
인접 행렬 : 그래프에 간선이 많이 존재하는 밀집 그래프
인접 리스트 : 그래프에 간선이 적게 존재하는 희소 그래프
https://freestrokes.tistory.com/87
Java 인접행렬과 인접리스트를 이용하여 그래프 구현하기
Java 인접행렬과 인접리스트를 이용하여 그래프 구현하기 Java로 인접행렬과 인접리스트를 만들어 그래프를 구현하는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 1. 그래프 (Graph) 수학적 정의로 그래프는 객체
freestrokes.tistory.com